The Market Equilibrium Fallacy Part 2
January 6, 2022 9 minutes • 1709 words
Table of contents
Supply and Demand Together
We combine both curves to come up with a Supply and Demand model.
Samuelson’s Version
Samuelson justifies the unnatural supply curve with buying and selling through an auctioneer scenario. This is the same sophistical technique used by Jevons and Marshall, in their attempt to justify equilibrium.
This is obviously false because no one goes to a grocery store to outbid other shoppers for every potato or loaf of bread. Neither do we make bids when we get drinks from a vending machine.
In reality, we as shoppers, have freedom to choose where we do our groceries and which vending machine to get our drinks. It is the groceries and vending machine companies that must compete with other sellers for our attention and choice.
From trial and error, Samuelson ends up with an equilibrium point where both curves intersect:
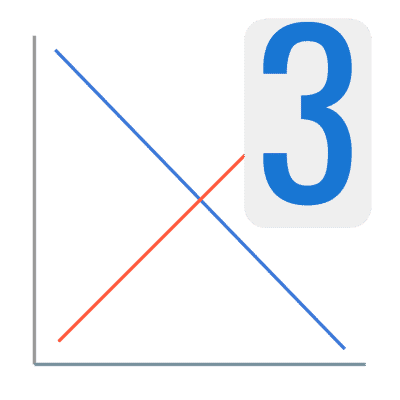
However, it is interesting to note what he says about what happens at low prices:
This is Samuelson’s second fallacy because:
- A product can only be sold cheaply if it is produced cheaply.
- It can only be produced cheaply through economies of scale.
- If it has economies of scale then there can be no shortage.
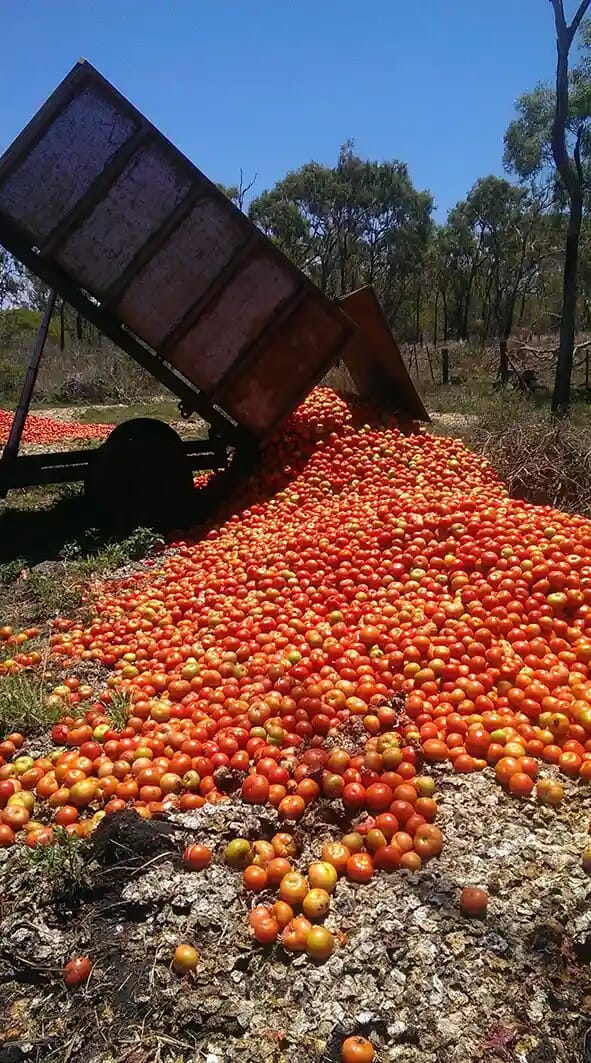
In fact, there are many cases of crops being overproduced and merely dumped. If wheat falls to $1, then it means that its production was plentiful, opposite of Samuelson’s assertion that storehouses will begin to empty.

The Mercantile Version
Like economist’s supply curve, the mercantilist’s supply curve also slopes upward.
Similarly, the mercantilist advocates reducing supply to increase the selling price, and cutting costs to increase profits.
By replacing ’exports’ with ‘sales’, and ‘imports’ with ‘purchases’ or ‘costs’, we can see that the merchant does the same things that the manufacturer does. What the manufacturer calls ’equilibrium’ is called ‘balance’ by the merchant, while ‘profit maximization’ is ‘overbalance’ or trade surplus*.
*The principle of the balance of trade is destroyed by the fact that the US is a net importer but is rich, while China was a net exporter back in the 2000’s but was relatively much poorer. If the balance of trade were strictly enforced, then the US should have started a total trade war with China back in the 2000’s to avoid being a net importer. Similarly, equilibrium is destroyed by the fact that a poor person can buy a $1 anti-parasitic medicine (of low nominal value) which will save his life (have maximum real value). If equilibrium were strictly enforced, then the seller of the $1 medicine should raise its price to $10,000 to be in equilibrium to the future lifetime productive value of the poor man. Alternatively, the seller can auction it to raise its price above $1 and maximize profits. All these propositions are absurd.
Smith’s Version
Unlike Samuelson who takes the position of the seller, Smith takes the position of the buyers. This is why profit maximization* never enters Smith’s curves.
*Instead of profit maximization as producer’s surplus, buyers are interested in bargains as consumer’s surplus
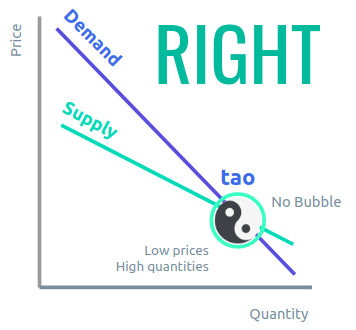
Unlike the curves of the manufacturer and merchant, Smith’s curves slope downwards to create low prices because it views economic activity as ultimately for the demanders or consumers, and not for the suppliers or sellers.
An Inherent Contradiction Leading to Systemic Crises
As you can see in the chart above, the sweet spot of the natural supply and demand is on the lower right section, representing high quantities at low prices.
However, the profit maximization doctrine of Economics teaches that:
- supply must be reduced so that prices will rise
- competition should be stifled in order to preserve one’s monopoly position so that high profits can be guaranteed to the investors.
The resulting high prices and low supply then contradict the goal of economic growth, especially after bubbles and financial crises.
Economists try to save face by saying that perfect competition is needed for it to work. But they do not realize that their supply curve makes perfect competition impossible in the first place. Because of this, ‘real equilibrium’ is never achieved despite the best efforts of economists and governments.
Worse is that the ecconomists and policymakers had no idea that their policies and theories were devised by the vested interests of traders, manufacturers, and financiers to benefit traders, manufacturers, and financiers. Such people only want maximum wealth for themselves, not knowing of the problems that excessive wealth creates:
When a potter becomes rich he will not think of you as much as before, grow more and more indolent and careless, and become a worse potter. But, on the other hand, if he has no money, he cannot provide himself with tools or instruments, he will not work well, and he will not teach his sons or apprentices to work well.
Then, under the influence either of poverty or of wealth, workers can degenerate. Here, then, is a discovery of new evils of wealth and poverty, against which the guardians will have to watch, or they will creep into the city unobserved. Wealth is the parent of luxury and indolence. Poverty is the parent of meanness and viciousness. Both are parents of discontent. Simple Republic Book 4
The Solution: Natural Price Theory and Economic Democracy
Adam Smith specifically pointed to the selfish-interests of traders, manufacturers, and financiers as the origin of the concept of market equilibrium:
The proposal of any new commercial law which comes from this order, should always be listened to with great precaution.It should never be adopted until after long and careful examination with the most scrupulous and the most suspicious attention.
The solution is a new paradigm that values all of society:
- the wage earners: workers, employees
- the profit earners: traders, manufacturers, financiers, farmers
- the rent earners: government, landlords, intellectual property holders, stockholders, asset owners
- the donation earners: religions, researchers, charities, NGOs, news companies, artists
By exposing the sophistical ideas such as equilibrium and profit maximization, we can say that Economics from the 1870’s is actually a corrupt science, and not merely a dismal one. It descended directly from Mercantilism which caused so much suffering in the colonies in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, and is still creating suffering nowadays through inequality, high prices, college debt, high taxes, etc.
Rather than reform a system with a corrupt base, it would be better to take its data and findings, and transplant them onto a new and proper one that is in line with the interests of society and human life.
For this reason, we introduce alternatives to every major economic concept as the foundation of Superphysics:
- Natural Price Theory replaces Equilibrium Theory of Microeconomics
- The Effort Theory of Value replaces Profit Maximization
- Purchasing Power replaces GDP of Macroeconomics
- Economic Balance replaces GDP growth







