Aethereal Territory: Quantum Fields
December 10, 2024 3 minutes • 576 words
Table of contents
In Modern Physics, a quantum field is a mathematical construct that exists throughout space and time.
Each type of particle (e.g., electrons, photons) corresponds to a specific field and are seen as excitations of them.
Instead of Quantum Fields, Material Superphysics uses aethereal territories to describe the behavior of subatomic particles.
| Physics | Physics Description | Superphysics Equivalent | Superphysics Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | is an excitation of the electromagnetic field | mor | vortex in the radiant layer |
Physicists see Quantum Mechanics as weird or spooky because they are stuck with materialist thinking that everything is within space.
But in Superphysics, all particles have a wave nature that is based on the aethereal layer, which then ‘wraps’ around the other layers. This includes spacetime.
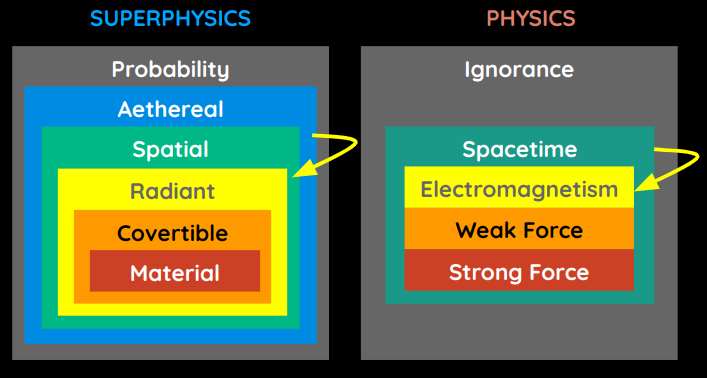
The aether itself is within probability the probabilty layer. This is why quantum mechanics, and reality itself, is inherently probabilistic.
This concept is imbued in the concepts of wave-paricle duality which is the cause of the following phenomena:
- superposition
- decoherence and wave function collapse
- entanglement
Superposition and Decoherence
Superposition is the ability of a quantum thing to exist in multiple states simultaneously. This is because everything is an aethereal wave.
This wave becomes a single state whenever it hits something. You can think of this as taking a snapshot of an event. The photo is the ‘collapse’ of the event-data just as a particle is the collapse of the wave.
Decoherence is the state after that thing loses its superposition through that collapse.
Entanglement
However, in Material Superphysics, all particles have a wave nature. They take the form of particles because of the confinement of the Negative Force on the observer’s aethereal mind, and even the detectors that are detecting those paricles.
“Entangled photons” really mean photon-waves that have been separated in space. They affect each other regardless of distance because the radiant layer (and the 2 lower layers) are within or under the spatial layer.
These happen through the coordination of the 3 sublayers of the spatial layer:
- Spacetime
- Aetherspace
- Timespace
Space-Time
Space-Time is similar to the spacetime of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity in the sense that it is made up of more than 3 dimensions.
Both Physics and Superphysics have a 4-dimensional spacetime with past, present, and future.
However, the Space-Time of Superphysics has additional dimensions:
- 5th Dimension as alternate realities
- 6th Dimension as parallel other universes
- 7th Dimension as the totality of existence
All these Dimensions are made up of 2-dimensional slices separated by Planck length.
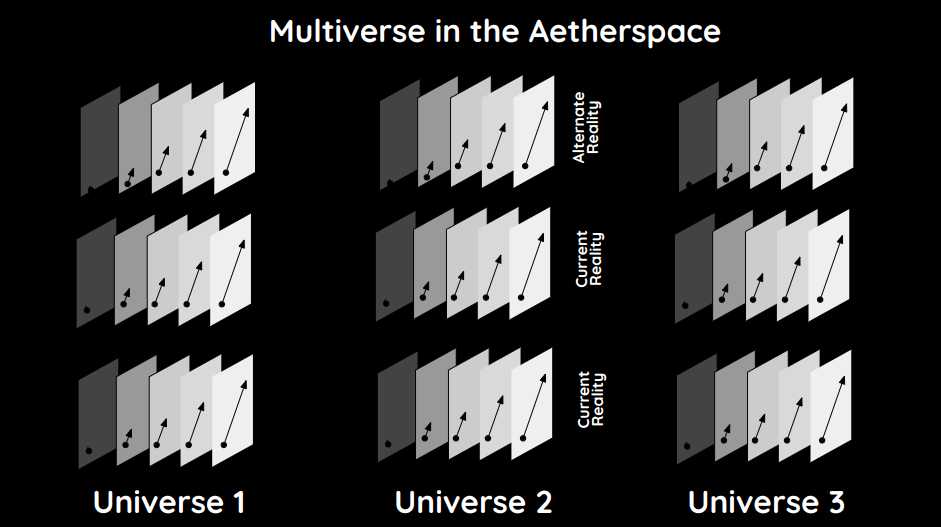
Aetherspace
These spacetime slices exist as a wave in a probabilistic space called the aetherspace. This makes them coherent and is why our reality progresses sequentially smoothly instead of being choppy or laggy.
It is the aetherspace that limits both spacetime and light to a certain speed.
Timespace
Timespace is the 2-dimensional line that is emitted from every identity in spacetime. This creates the “arrow” of time.
We can say that timespace is the ‘glue’ that stitches spacetime together to create a 4D continuum.
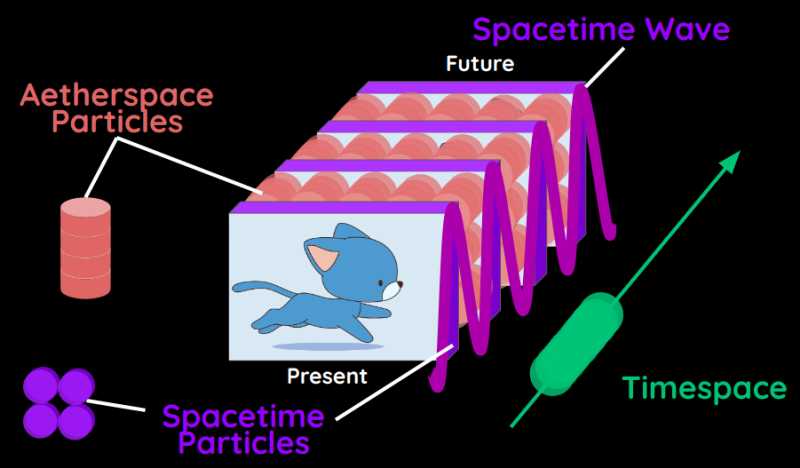
Interactions between quantum things cause these slices to be decoherent. This makes their wave function collapse according to the timespaces that interact in that aetherspace, putting them in a single state to be processed by Classical Mechanics, among others.







