Principle of Least Action or Effort
3 minutes • 639 words
Table of contents
Material Superphysics is based on Cartesian and Asian Physics which says that energy and forces come from outside that work through the internal configuration of an identity.
This internal configuration is called the gravitational signature.
An analogy is:
- a quantum of identity as a washer
- a medium is a screw
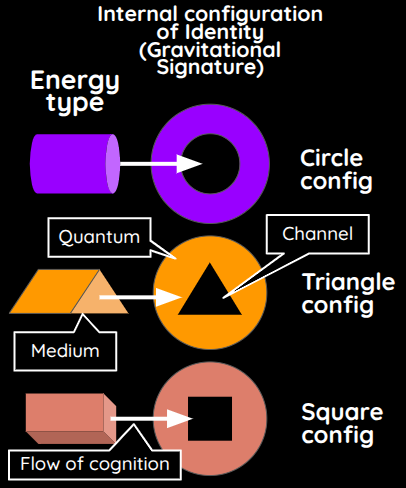
The energetic screw fits into the washer transferring the energy to it. This allows the identity to act, as spin.
This means that all energies come from space which flow into each particle. More energy can be obtained by matching the internal configuration with the desired energy or force external.
For example, electricity is able to get energy from space around the wire through the presence of electrons which act as a channel for the virtual photons in space.
So the sequence is:
- Identity settles on a configuration
- This configuration allows energy to go through the identity
- The energy causes the identity to spin or act based on its nature or layer and sublayer
We call this process as “Effort”.
This is the meaning of our equation for everything, which we call the Eagle:

Action is Effort
In Physics, the concept of Action is most similar to Effort, which is different from Energy and Force.
- Energy is the medium before it enters the identity
- Force is the effect of the effort on the identity
So the sequence is:
- Energy
- Effort
- Force (if there is another object to move or be moved, or act on or be acted on)
How Physics Came Up With Action
The concept of action was realized by Descartes from the phenomena of colors.
Colors are created whenever:
- light bounces off an object
- colored light is emitted from an object
For example, a dark room will have all its objects as black. But when you turn on a light bulb:
- the aetherspace in the atoms of the filament causes light to have a yellow or white color depending on the spin of the electrons
- the light bouncing off from the objects causes the photons to spin differently, revealing different colors.

In this example:
- the spin of the electron in the light bulb determines the color of the light
- the spin of the reflected photons determines the color of the object.
Here, the spin dictates colors which is an effort or action of the photon. Light has other efforts or actions:
- information-carrier as pulses
- force-carrier as brightness
- spread as invariance
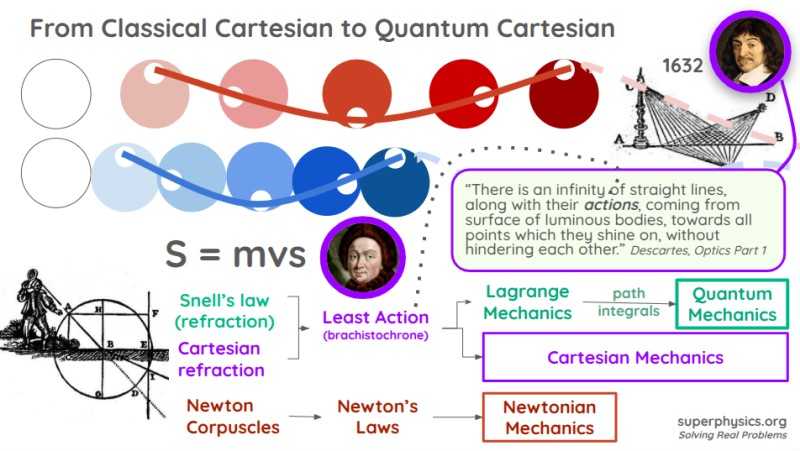
Maupertuis denoted this action as S = mvs.
The path that the light will take is then determined as the one that takes the least time. This creates the Principle of Least Action.
Euler then converts this into integrals, while Lagrange adds multipliers. This creates Lagrangian mechanics.
Unlike F = ma which uses external forces to explain motion, Euler-Lagrange uses internal action or effort.
Descartes calls this true motion which is sourced from the relation of an object’s action (based on its spin) to the actions of other objects (and their spin). This relation is what we see as force.
- Planck used the energy of light (which is one action) to create Planck’s constant.
- Einstein used the the invariance of light (another action) to create Relativity.
- Feynman used probability of path integrals (which is actually the action of the aether instead of light) to create quantum mechanics.
Feynman wrongly used relativistic time (which is an action of light instead of the aether) in path integrals. This created infinities which people tried to solve with Supersymmetry and String Theory.
Descartes already solved this by adding the aether and its actions.
But this was unsolved by Einstein who only knew light actions and so he made time an action of light instead of the aether through his scam simultaneity of time. This has set back Physics by over 100 years.







